Overview of VoIP Gateways
What is VoIP Gateways
A VoIP gateway is a network device which converts analog telephony traffic from the PSTN (Publicly Switched Telephone Network) into digital packets IP packets for transport over an IP network and Vice versa.
How does a VoIP gateway work?
To know working of VoIP gateways is very simple, it works as a bridge between an IP network and the PSTN. Depending on where the voice traffic originates from a VoIP gateway will convert the voice traffic into the proper form by the destination network IP or PSTN.
- If the voice traffic is originating from the PSTN the VoIP gateway will convert the analog voice signal into a digital signal. This digital signal is then compressed using a codec and broken into a series of packets that are transferred across the IP network using a signaling protocol.
- If the voice traffic is originating from an IP network the VoIP gateway will decompress the digital packets into a digital signal that is then converted into an analog signal to be sent across the PSTN.
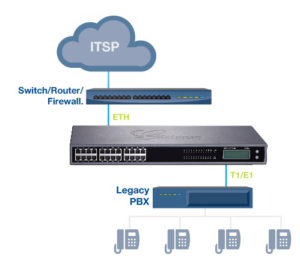
Using a gateway to connect a VoIP phone system to traditional phone lines makes sense in situations where SIP trunks are not available or where your application requires the reliability of the PSTN. It also makes it easy to build redundant systems. The gateway normally communicates with a primary IP PBX. In the event of a failure on the primary, the gateway can communicate with a backup system.
Other uses for VoIP gateways include staged migrations, where the gateway acts as a bridge between the PSTN, a legacy PBX and a new IP PBX. In this case, the PSTN trunks are connected to one interface on the gateway. Another interface connects to the trunk port on the legacy PBX. The new IP PBX is integrated over a VoIP protocol (generally SIP). The gateway directs some incoming calls to the legacy PBX and others to the IP PBX. It also passes calls between the two PBXs. This allows some department or other subdivisions of the company to remain on the legacy system while others move to the IP system.
Different Types of VoIP Gateways:
There are two types of VoIP Gateways you want to know and learn
- Analog Gateway
- Digital Gateway
Analog Gateways:
An analog VoIP gateway is used to connect your traditional analog telephones PSTN to a VoIP phone system or vice versa. In simple words, Convert Incoming PSTN / Telephone Lines to VoIP/SIP
Due to this dual purpose an analog VoIP gateway comes in two different forms
- FXS gateway (Foreign Exchange subscriber)– An FXS gateway is used to Convert Incoming PSTN / Telephone Lines and Fax machines to VoIP/SIP system
- FXO gateway(Foreign Exchange Office) – An FXO gateway is used to connect your VoIP phone system to your PSTN lines
Digital Gateways:
A digital VoIP gateway is used to connect your VoIP Phone system to your digital voice lines such as T1/E1/BRI. A digital VoIP gateway can also be used to connect your traditional PBX system to an IP network. In simple words, Connect a Traditional PBX / Phone System to the IP Network
We are focusing on Analog gateways in this session, let us know more about its features
General Features of VoIP Gateways:
Characteristics of VoIP gateways are different from each type, there are few general features which are commonly found in all the gateways are
- FXS ports with PSTN life line in case of power failure
- SRTP security protection
- Switch mode or Router mode network port
- Codec Support
- Call routing, packetization and control signaling management
- Voice and T.38 fax compression/decompression
- External controller interfaces
Click here for Continuation of VoIP Gateways

